Research
The integration of distributed energy resources (DERs), including photovoltaic power generation (PV) and electric vehicles (EVs), is indispensable for achieving a decarbonized society. However, it is necessary to address various problems caused by the integration of DERs into the distribution networks, such as voltage overloads and congestion of distribution lines. Our laboratory aims to build a sustainable society through research on energy management systems (EMSs) for constructing smart grids that enable the massive expansion of DERs and promote carbon neutrality.
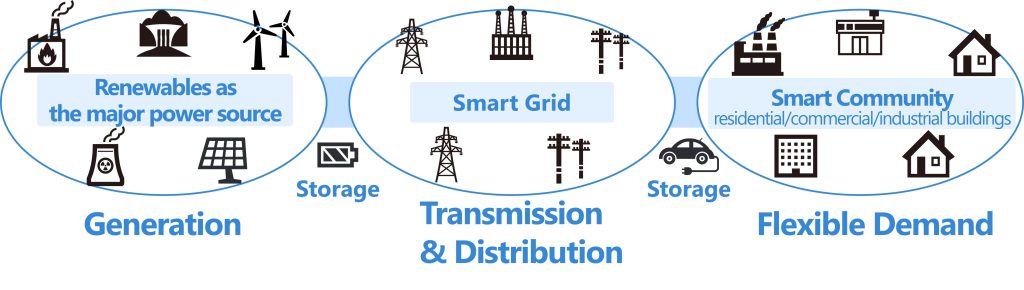
Construction of “Electricity × Transportation sector coupling model”
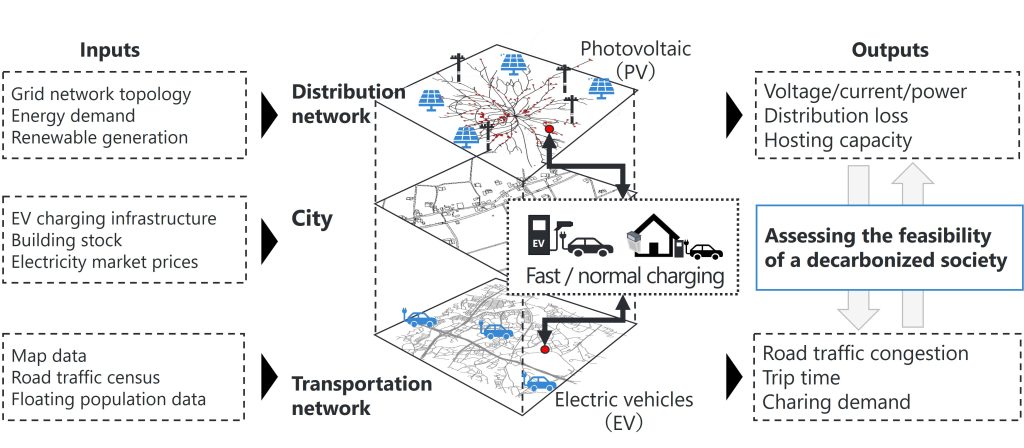
To achieve carbon neutrality, it is necessary to approach decarbonization from the perspective of both energy demand and supply, which requires the use of renewable energy as the primary power source and thorough energy conservation and electrification in the industrial, consumer, and transportation sectors. When considering the introduction of electric vehicles, we must devise approaches that maximize the utilization of renewable energy instead of relying on electricity derived from fossil fuels for charging. This requires constructing a sector-coupling model that reflects interactions between the distribution network on the energy supply side and the transportation network on the energy demand side.
In our laboratory, we are focusing on constructing an “Electricity × Transportation Sector Coupling Model” that replicates the electrical behaviour of distribution networks and vehicle dynamics of the transportation network in urban cities. This model incorporates various data inputs, including information on grid and transportation networks, electricity generation and demand, meteorological patterns, and floating population demographics, to quantitatively evaluate the performance of developed EMSs from various perspectives such as voltage stability of distribution networks and CO2 emissions. We aim to establish an evaluation framework for identifying challenges toward decarbonization and assessing the feasibility of achieving a decarbonized society. Furthermore, we are considering various applications for further research and development.
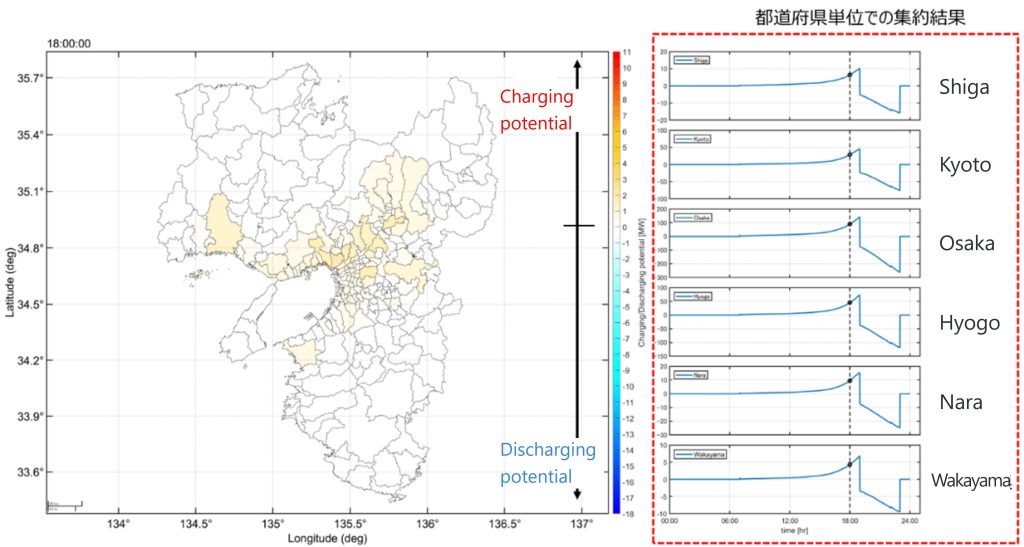
Impact analysis of distributed energy resources on distribution networks
To make renewable energy the primary power source and to achieve carbon neutrality, it is essential to quantitatively estimate the potential contribution of distributed energy resources and assess their impact on the distribution networks. With the increasing use of electric vehicles, we utilize latitude-longitude point sequence data acquired through GPS on smartphones to simulate the driving and charging/discharging patterns of electric vehicles. This simulation helps us estimate the potential charging/discharging capability for electric vehicles.
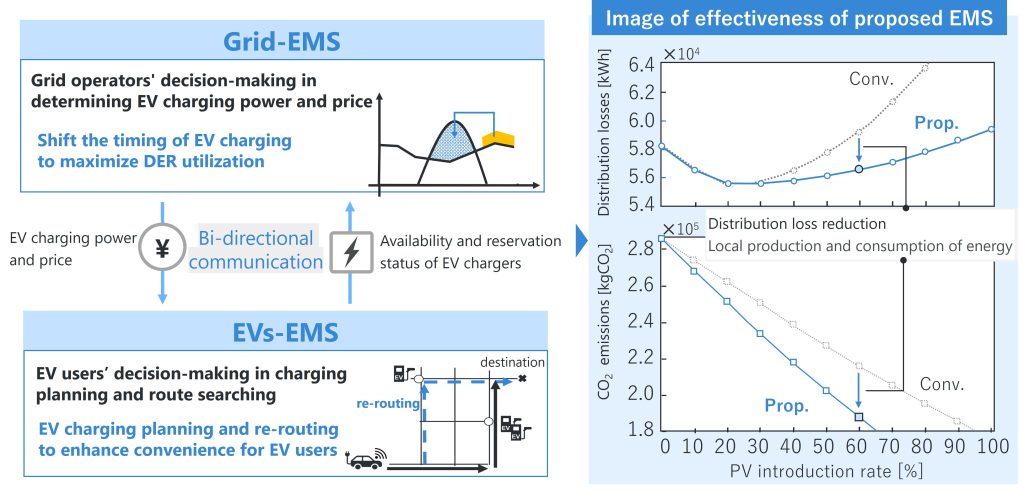
Development of energy management system for expansion of distributed energy resources
Our laboratory focuses on next-generation distribution network stabilization technology that utilizes the grid-support functions in distributed energy resources. We aim to develop new approaches to reduce distribution losses and electricity costs while maintaining power quality, such as voltage and frequency. We are also developing energy management systems that concurrently maximize the utilization of renewable energy and enhance convenience for electric vehicle users by incorporating real-time information obtained through bidirectional collaboration between distribution system operators and electric vehicle users.